ERP vs MRP: Key Differences and Benefits.
As the manufacturing business getting complex, there are software that claims as ERP Software or MRP Systems etc. This is leading to confusion in the people mind. Technically, the MRP module is part of an ERP Software as the ERP is for the complete Enterprise wide data management. However companies need not deploy an ERP and they are happy with a subset of ERP features like MRP Settings. So understanding ERP vs MRP or MRP vs ERP is important as it guides towards what features we need to buy.

Note – Few customers consider MRP as “Manufacturing Resource Planning” too.
A list of common features are listed below for a manufacturing industry that gives a real-time visibility
- Shop floor control
- Human capital management with Payroll.
- Supply chain management with Warehouse management
- Sales and Purchasing activities– Track Materials from suppliers and ensure to invoice them to customers.
- Inventory control – Raw Materials, Finished Goods, Consumable etc. This helps with inventory costs and Stock control
- Capacity planning with Production schedule with manufacturing process. It helps with tracking of production operational costs
- Customer relationship management
- Project management with Customer management
- Materials management with Operational processes
- Business intelligence tools.
- Quality assurance
- Accurate forecasting of needs.
What is MRP System?
An MRP system, or Material Requirements Planning system, is a pivotal tool used by manufacturing companies to manage their production processes and inventory levels efficiently. This system facilitates the planning and scheduling of raw materials, components, and resources needed to meet production demands and maintain optimal inventory levels. By analyzing data related to sales orders, production schedules, and inventory levels, MRP systems ensure that manufacturers have the right materials available at the right time to fulfill customer orders and minimize production disruptions.
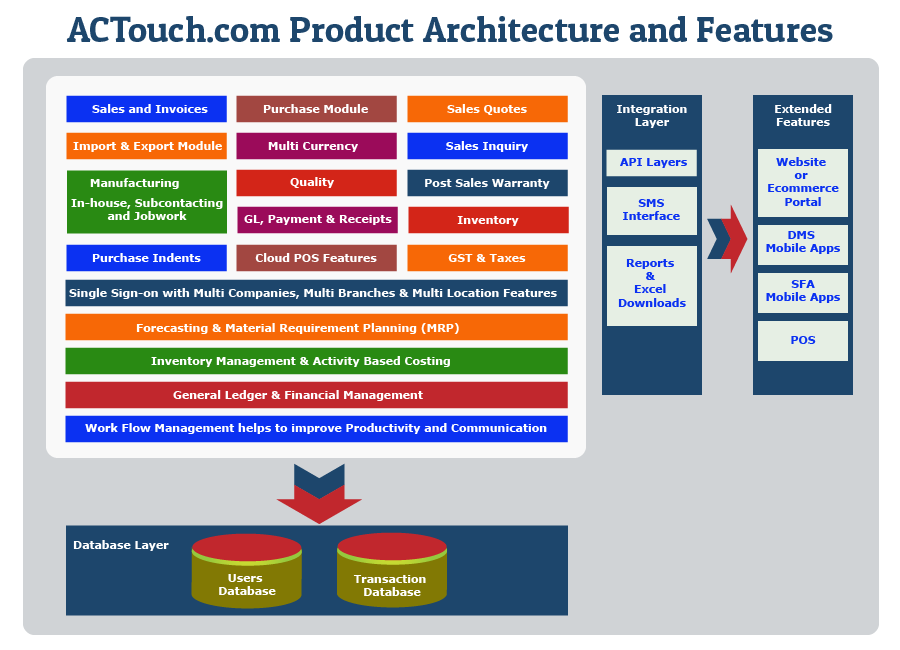
MRP System Meaning
The meaning of MRP system lies in its ability to streamline the production process by calculating the exact quantities of materials needed for manufacturing, taking into account factors such as lead times, order quantities, and production schedules. It translates sales forecasts and customer orders into actionable plans for purchasing and production, ensuring that manufacturers can meet customer demands without overstocking or understocking inventory.
What is MRP Definition?
The definition of MRP, or Material Requirements Planning, refers to a systematic approach that manufacturing companies use to manage and plan the materials needed for production. MRP calculates the exact quantities of raw materials and components required based on production schedules, sales orders, and inventory levels. This enables manufacturers to optimize their material procurement, reduce wastage, and improve overall production efficiency.
|
What is MRP Software?
What is MRP Software?
MRP software, or Material Requirements Planning software, is a sophisticated digital tool designed to assist manufacturing companies in efficiently managing their production processes and inventory levels. It combines data analysis, calculations, and automation to facilitate precise material planning, order scheduling, and inventory control. This software helps manufacturers ensure that the right materials are available at the right time, minimizing wastage, optimizing production, and meeting customer demands effectively.
Example 1: Calculating Material Needs
Let’s consider a furniture manufacturing company. They receive orders for various types of furniture, each requiring different raw materials such as wood, fabric, and hardware. The MRP software takes into account the production schedules, order quantities, and lead times. It then calculates the exact quantities of each material required to fulfill the orders. For instance, if the company receives an order for 100 chairs, the MRP software calculates that it needs 500 square feet of wood, 200 yards of fabric, and 400 pieces of hardware. This precision prevents overordering and reduces excess inventory.
Example 2: Managing Production Schedules
An electronics manufacturer has a range of products with different production times and lead times for components. Using MRP software, the company can input sales forecasts and production schedules. The software then generates a production plan that aligns with demand and ensures that components arrive on time for assembly. If a specific component has a longer lead time, the software can trigger orders well in advance to avoid production delays. This proactive approach streamlines the production process and minimizes disruptions.
Example 3: Preventing Stockouts
A pharmaceutical company manufactures a range of medications. With varying demand and regulatory constraints, it’s critical to have the right ingredients in stock. MRP software continuously monitors inventory levels and compares them to sales orders and production schedules. If the software predicts that a particular ingredient is running low and won’t meet future demand, it generates a purchase order to replenish the stock. This prevents stockouts, ensures consistent production, and maintains customer satisfaction.
Example 4: Adjusting for Fluctuations
A clothing manufacturer experiences seasonal fluctuations in demand. During peak seasons, they receive a surge of orders for specific clothing items. MRP software can analyze historical sales data to predict these seasonal spikes. As the high-demand period approaches, the software adjusts production schedules and material orders to ensure that the necessary materials are readily available. This prevents bottlenecks and allows the manufacturer to capitalize on peak sales periods.
Example 5: Cost Optimization
An automotive parts manufacturer sources materials globally. Fluctuating exchange rates and shipping costs can impact the overall cost of production. MRP software considers not only material quantities but also factors in costs. It assesses the most cost-effective suppliers and shipping options, helping the company make informed decisions to optimize costs while maintaining quality.
MRP software is a vital tool that empowers manufacturing companies with accurate material planning, production scheduling, and inventory control. By analyzing data and automating calculations, MRP software enables manufacturers to operate efficiently, minimize waste, meet customer demands, and stay competitive in the dynamic business landscape.
What is the Difference Between ERP vs MRP?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and MRP (Material Requirements Planning) are two distinct but interconnected systems used by manufacturing companies to manage their operations, resources, and materials. While both systems contribute to efficient production processes, they have different scopes and functionalities that cater to various aspects of business management. Here’s a more detailed look at the differences between ERP and MRP:
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning):
ERP is a comprehensive software solution that integrates various business processes and functions across an organization into a centralized system. It goes beyond the realm of production and inventory management, encompassing finance, human resources, sales, procurement, customer relations, and more. The primary goal of ERP is to offer a holistic view of an organization’s operations, enabling better communication, data sharing, and decision-making across departments.
MRP (Material Requirements Planning):
MRP, on the other hand, is a subset of ERP that specifically focuses on the planning and scheduling of materials required for production. MRP software calculates the exact quantities of raw materials, components, and resources needed to meet production demands. It takes into account factors like sales orders, production schedules, lead times, and inventory levels to ensure that materials are available when needed, minimizing wastage and optimizing production efficiency.
Key Differences:
- Scope:
- ERP covers a wide range of business processes beyond production, including finance, HR, sales, and customer relations.
- MRP is exclusively concerned with material planning and inventory management within the production process.
- Functionality:
- ERP provides integrated tools for managing various aspects of a business, such as financial transactions, employee management, and customer interactions.
- MRP focuses on calculating material requirements, generating production schedules, and ensuring timely material availability for manufacturing.
- Integration:
- ERP integrates multiple departments into a centralized system, promoting data consistency and enhancing communication between various functions.
- MRP primarily integrates with the production and inventory management aspects of a business.
- Scope of Impact:
- ERP impacts the entire organization, from front-end customer interactions to back-end financial reporting.
- MRP primarily impacts the production process by ensuring that materials are available to meet production schedules.
- Decision-Making:
- ERP supports overall business decision-making by providing insights into various operational aspects.
- MRP supports production decision-making by calculating material requirements based on production plans and sales orders.
- Complexity:
- ERP systems tend to be more complex and comprehensive due to their wide range of functionalities.
- MRP systems are more focused and streamlined, centered around material planning and scheduling.
In essence, ERP and MRP are interconnected tools that serve different but complementary functions within a manufacturing company. While ERP provides a holistic overview of the organization’s operations, MRP specializes in optimizing material availability for efficient production.
How MRP System Helps Manufacturing Companies?
MRP systems offer significant benefits to manufacturing companies:
- Optimized Inventory Management: MRP systems prevent overstocking or stockouts by calculating precise material requirements, minimizing carrying costs, and ensuring timely material availability.
- Reduced Lead Times: By accurately predicting material needs, MRP systems help streamline production schedules, reducing lead times and enhancing overall production efficiency.
- Minimized Wastage: MRP systems help manufacturers order or produce only the required quantities of materials, reducing wastage and conserving resources.
- Improved Production Planning: MRP systems enable manufacturers to plan production based on actual demand, ensuring that products are available when customers need them.
Advantages of ERP and MRP
Both ERP and MRP systems offer unique advantages to manufacturing companies:
- Efficiency: ERP systems streamline business operations by integrating various departments, improving communication, and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Data Visibility: Both systems provide real-time data insights, empowering informed decision-making and enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Resource Optimization: MRP systems optimize material resources, while ERP systems extend this optimization to other areas such as finances, human resources, and customer relations.
- Centralized Information: ERP systems offer a centralized repository of data, reducing data duplication and ensuring consistent information across the organization.
- Scalability: Both systems can scale as manufacturing companies grow, accommodating increased production volumes and operational complexities.
MRP systems play a crucial role in managing material inventory and production planning within manufacturing companies. They ensure that the right materials are available at the right time to meet customer demands efficiently. When integrated into ERP systems, the benefits extend beyond production to encompass various business processes, resulting in streamlined operations, improved resource utilization, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.

