ERP Guide: Expert Guide to select ERP, Choose Vendor and Implement it.
What is ERP Guide?
An ERP Guide serves as a comprehensive roadmap for businesses navigating the complex world of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. It’s a valuable resource designed to provide insights, strategies, and expert advice on successfully implementing and utilizing ERP software. ERP solutions integrate various business processes, streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
Navigating the world of ERPs without a guide can be overwhelming. A well-structured ERP Guide helps businesses understand the nuances of ERP implementation, customization, and usage. It addresses common challenges, offers best practices, and equips businesses with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
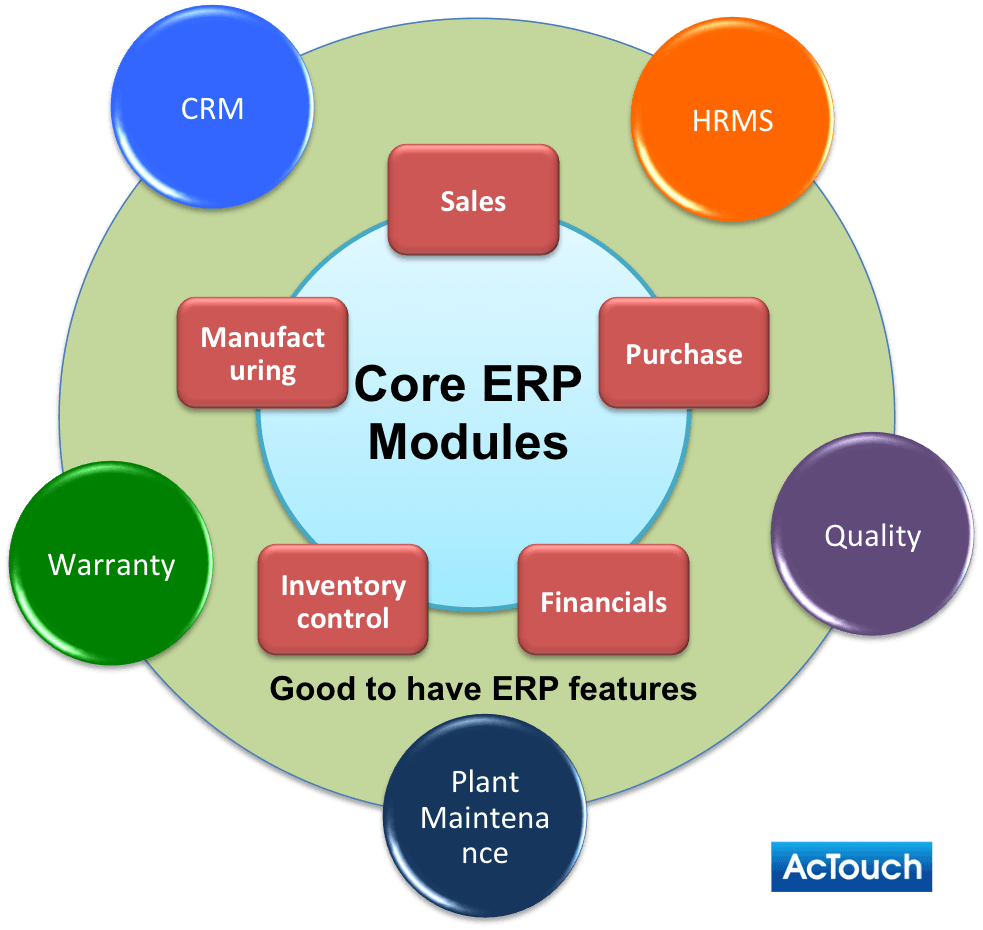
What are ERP Modules? Explain how ERP guide can help?
Business units adopt enterprise resource planning software systems consist of various interconnected modules or core business processes that cater to different functional areas of an organization. These modules are designed to work seamlessly together, sharing information and ensuring real-time data availability across the enterprise. Some key ERP modules include:
- Finance Module: Manages Financial management, accounting, and budgeting.
- Human Resources (HR) Module: Handles employee information, payroll, and recruitment.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Module: Manages procurement, inventory, and logistics.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module: Focuses on managing customer interactions and improving relationships.
- Sales and Marketing Module: Tracks sales activities, campaigns, and customer interactions.
- Manufacturing Module: Manages production processes, scheduling, and quality control.
- Inventory management
- Project management – Implementation team with implementation projects activities
Each module caters to specific business functions, ensuring a holistic approach to managing operations.
Give a Check list to Evaluate an ERP?
Evaluating an ERP is a critical process. Use this checklist to make an informed decision:
- Business Alignment: Does the ERP meet your organization’s specific needs and goals?
- Functionality: Does it offer the essential features your business requires? How about training costs? How easy to map our business models and business requirements. Do we need to do any Customizations?
- Scalability: Can it accommodate your business growth over time?
- Integration: Can it seamlessly connect with your existing systems? Is this Enterprise resource planning systems has API for us to integrate?
- User-Friendliness: Is the interface intuitive for your employees?
- Customization: Can it be tailored to your unique processes?
- Vendor Reputation: Does the ERP vendor have a proven track record? How is their implementation team? Do they understand your business?
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider both upfront and ongoing costs. What is the Upfront costs of the project? Is it clearly defined and understood?
- Support and Training: Evaluate vendor’s support and training offerings.
- Security and Compliance: Does it adhere to industry standards? Is this a single common database or Multi-DB environment? Is it private cloud or not? Is it 100% cloud-based ERP or not?
|
What are the Advantages of ERP?
Implementing an ERP offers numerous advantages, including:
- Streamlined Processes: ERPs automate workflows, reducing manual tasks and improving efficiency.
- Data Centralization: All departments access real-time data, fostering better decision-making.
- Improved Collaboration: Teams can collaborate seamlessly, enhancing productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: CRM modules improve customer interactions and satisfaction.
- Accurate Reporting: ERPs generate insightful reports, aiding strategic planning.
- Cost Savings: Automation reduces operational costs and eliminates redundancies.
- Scalability: ERPs adapt to business growth, preventing the need for frequent changes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Modules ensure adherence to industry regulations.
- Data Security: ERPs offer robust security features to protect sensitive information.
How you differentiate between On-premise ERP and Cloud ERP?
On-premise ERP: This traditional model involves hosting the ERP software on your own servers. It requires substantial upfront investments in hardware, infrastructure, and maintenance. On-premise ERPs provide greater control over data and customization but may lack scalability.
Cloud ERP: Cloud-based ERPs are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. They offer flexibility, scalability, and reduced initial costs. Updates and maintenance are handled by the provider. Cloud ERPs are ideal for businesses seeking quick implementation and lower capital expenditure.
Why should we choose our Cloud ERP?
Choosing a Cloud ERP offers several benefits:
- Lower Initial Costs: Cloud ERPs have minimal upfront expenses.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources based on business needs.
- Faster Implementation: Cloud ERPs can be up and running quickly.
- Automatic Updates: Providers handle updates and maintenance.
- Remote Access: Access your ERP from anywhere with an internet connection.
How to evaluate an ERP vendor?
Evaluate ERP vendors based on:
- Experience: Look for vendors with a proven track record in your industry.
- References: Check client references and success stories.
- Product Fit: Ensure their ERP aligns with your business needs.
- Support: Assess their customer support responsiveness.
- Scalability: Choose a vendor that can grow with your business.
- Customization: Check their ability to tailor the ERP to your processes.
- Security: Verify their data security and compliance measures.
What are the criteria for selecting ERP?
Criteria for selecting an ERP include functionality, scalability, integration capability, user-friendliness, customization options, vendor reputation, cost considerations, support and training, security and compliance, mobile accessibility, and reporting capabilities.
5 steps for a successful ERP implementation, a guide to ERP implementation?
- Planning: Define objectives, scope, and resources.
- Vendor Selection: Choose a suitable ERP and vendor.
- Data Migration: Migrate existing data to the new system.
- Customization and Testing: Customize the ERP and conduct thorough testing.
- Training and Adoption: Train users and ensure smooth adoption.
How do you assess the success of ERP Implementation?
Assess ERP implementation success through ERP guide and its reference is as below:
- User Adoption: Measure how well employees use the system.
- Improved Processes: Evaluate the efficiency of revamped processes.
- ROI: Calculate the return on investment achieved.
- Accuracy: Measure data accuracy and reduction in errors.
- Customer Satisfaction: Gauge if the ERP enhances customer service.
- Scalability: Determine if the ERP supports business growth.
FAQ: Exploring ERP Guide: Components, Phases, Life Cycle, and Cloud Benefits
1. ERP Guide: What are the 5 components of ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems consist of five core components:
- Hardware: This includes servers, computers, and networking equipment required to run the ERP software.
- Software: The ERP application itself, encompassing various modules for different business functions.
- Data: The information entered, stored, and processed within the ERP, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Procedures: The predefined workflows and processes that guide how data is captured, processed, and reported.
- People: The individuals who operate, manage, and use the ERP system, ensuring its effective utilization.
2. ERP Guide: What are the 6 phases of ERP Implementation?
The ERP implementation process typically involves six phases:
- Project Preparation: Defining the scope, objectives, and teams for the ERP project.
- Business Process Mapping: Analyzing existing processes and determining how they will align with the ERP.
- Data Migration: Transferring data from old systems to the new ERP.
- Configuration: Customizing the ERP to match the organization’s processes and requirements.
- Testing: Rigorously testing the ERP to identify and rectify any issues.
- Deployment and Support: Launching the ERP and providing ongoing support to ensure its successful operation.
3. ERP Guide: What is the ERP life cycle?
The ERP life cycle encompasses various stages, from selection to eventual replacement:
- Initiation: Identifying the need for an ERP and planning the project.
- Selection: Choosing the appropriate ERP vendor and solution.
- Implementation: Installing and configuring the ERP to align with business processes.
- Training and Testing: Training users and thoroughly testing the system.
- Go-Live: Launching the ERP for daily operations.
- Support and Maintenance: Providing ongoing support, updates, and maintenance.
- Evaluation and Enhancement: Assessing the ERP’s performance and making improvements as needed.
- Replacement or Upgrade: Replacing the ERP when it no longer meets business needs or upgrading to newer versions.
4. Why should you choose Cloud ERP, guide to ERP software?
Opting for a Cloud ERP offers several compelling benefits:
- Lower Initial Costs: Cloud ERPs often have lower upfront expenses compared to on-premise solutions.
- Scalability: Cloud ERPs can easily accommodate business growth without significant infrastructure changes.
- Faster Implementation: Cloud ERPs can be deployed more quickly, reducing downtime.
- Automatic Updates: Providers handle updates and maintenance, ensuring you’re always using the latest version.
- Remote Accessibility: Cloud ERPs allow authorized users to access the system from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Reduced IT Overhead: Cloud ERPs require less internal IT management, freeing up resources for other strategic initiatives.
- Flexibility: Cloud ERPs offer flexibility to scale resources up or down based on fluctuating needs.
- Enhanced Security: Reputable cloud providers often invest heavily in security measures, ensuring data protection.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud ERPs offer built-in disaster recovery capabilities, safeguarding data in case of unforeseen events.
- Global Collaboration: Cloud ERPs enable seamless collaboration among teams across different geographical locations.

