What is inventory cost?
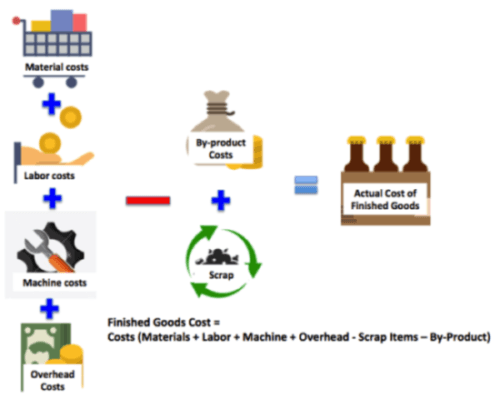
Below image gives an idea on the components that are required to arrive at the Finished Goods costing and also how to calculate the Inventory costing. Here we are making an attempt to explain the inventory cost and how its calculated etc?
Recently we spoke few Customers, who are worried about the increasing costs of doing the business. One of the factor was inventory cost and they were struggling to find the cost in a more proper and scientific way. So we asked few questions to find how the inventory costing is done by them?
- What’s your cost of Finished Goods? How you arrive?
- How much Raw Materials costs have increased in last one year?
- Whats the cost of labour or Machine costs that incur?
- How much is the Electricity and other expenses?
Many business owners have a fair idea of their Inventory Carrying cost of the raw materials and how much them goes into Finished Goods. But do they address the real costs?
No. Because customer Accounting software doesn’t allow. So how the inventory costing is done? What are the parameters to be considered?
So many business owners depend on Excel document with many parameters and these are identified at the time, when the Finished Goods (FG) Costing was arrived and when the Quote was given at the beginning. But as the time passes, the Raw materials (RM) cost goes up and these are not added back to FG Costing to arrive at the real cost and increase the FG selling cost. Many follow this below shown costing approach. We took an example of an Automobile Component manufacture that manufacturers and sell U-Bolts. The figures are fictional and not an actual
| No | Major Components | Details | Cost (Rs.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raw Materials | EN-8 materials of 100mm length and Dia16 mm | 100 |
| Packaging Material costs | 3.5 | ||
| 2 | Operation cost | Cutting | 2.00 |
| Bending | 2.00 | ||
| Threading | 5.00 | ||
| Hardening | 4.00 | ||
| Blackening | 1.00 | ||
| Packaging | 1.00 | ||
| 3 | Total cost of Finished Good | 118.50 | |
| 4 | Overhead costs | 30% of total cost | 35.55 |
| 5 | Profit Margin | 30% of the total Cost including Overhead cost | 46.25 |
| 6 | Total Selling price | 200.30 |
How to find Inventory Carrying Costs?
Inventory Carrying Costs, also known as holding costs or carrying costs, refer to the expenses incurred by a business to maintain and store inventory over a specific period. These costs are crucial for businesses to consider as they have a direct impact on the company’s profitability, working capital management, and overall operational efficiency. By understanding and managing inventory carrying costs, businesses can optimize their inventory levels and make informed decisions to improve their financial performance.
Elements of Inventory Carrying Costs
- Storage Costs: This includes expenses related to the physical space needed to store the inventory. It encompasses rent, utilities (electricity, water, heating/cooling), lease or mortgage payments, and property taxes for the warehouse or storage facility.
- Capital Costs: Capital costs represent the opportunity cost of tying up funds in inventory instead of using them for other investment opportunities. It includes the cost of financing inventory, such as interest on loans or the expected return on investment that could have been earned if the capital was invested elsewhere.
- Insurance Costs: Businesses need to insure their inventory against potential losses due to theft, damage, fire, or other risks. Insurance premiums are considered as part of the carrying costs.
- Handling Costs: These costs cover expenses related to the movement, handling, and management of inventory. It includes labor costs for receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping inventory items. Equipment used in the handling process, such as forklifts or conveyor systems, also contribute to these costs.
- Obsolescence and Depreciation: If inventory items have a limited shelf life or are subject to technological advancements, they may become obsolete or lose value over time. The costs associated with obsolescence and depreciation are part of the carrying costs.
- Pilferage and Shrinkage: Pilferage refers to theft or loss of inventory due to employee or customer theft, administrative errors, or damaged goods. The cost of pilferage and shrinkage is considered when calculating carrying costs.
- Opportunity Costs: This is the potential profit that could have been earned if the inventory was sold or used in production instead of being held in stock. Opportunity costs are closely tied to the concept of capital costs.
- Taxes and Regulatory Costs: In some regions, businesses may be subject to inventory taxes or other regulatory costs related to holding inventory.
Managing Inventory Carrying Costs
Effectively managing inventory carrying costs is essential for optimizing inventory levels and improving the company’s financial performance. Here are some strategies businesses can employ:
- Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting can help businesses maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing the need for excessive storage and minimizing associated costs.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Implementing JIT inventory management can help reduce holding costs by receiving inventory only when needed, minimizing storage space and capital tied up in inventory.
- Inventory Turnover: Monitoring inventory turnover helps identify slow-moving items, allowing businesses to make informed decisions on pricing, promotions, or liquidating old stock.
- Supplier Collaboration: Collaborating with suppliers can lead to more flexible ordering arrangements, reducing the need to carry excessive safety stock.
- Effective Inventory Control: Employing robust inventory control systems can help prevent overstocking and stockouts, optimizing inventory levels.
By understanding the elements of inventory carrying costs and implementing effective management strategies, businesses can strike a balance between maintaining adequate inventory levels to meet customer demand and minimizing the associated costs, ultimately improving their bottom line.
Inventory Holding Cost calculator
This is also called Inventory Carrying Cost calculator.
Use our free Inventory Holding Cost calculator
In this rough costing there are many things are missing
- Cost of raw materials – Typically RM price changes based on the demand and Supply. So the cost could go up or down. So the right model is to have a Weighted Moving Average Cost (WMAC) as it takes into the account the Past costs and also the Current purchase prices. ACTouch.com uses this model.
- Activity based costing – (ABC) – Each activities costs would increase depends on the labors who work on the machines. You can not take an Average cost as the employee costs changes every year and its advisable to take the actual labor costs that are used for those machining activities. This ensures that all the costs are factored.
- Subcontracting costs – If we are sending the materials to an outside agency that does hardening or blackening operations and these costs should to be added to your RM costs. Many customers don’t know how to do this?
- Other costs
- Furnace oil used for the operation
- Electricity consumed
- Other overheads
- Biggest problem is how these are added to the RM costing at the time of Conversion to FG?
Many SME Business Owners don’t follow this because their Accounting Software is old and doesn’t allow these dynamic changes.
Let’s check how ACTouch Cloud ERP can help here?
| No | Major Components | Details | Cost (Rs.) | Whats the problem? | How AcTouch.com helps? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raw Materials | EN-8 materials of 100mm length and Dia16 mm | 100 | Purchase price may change for Every Goods receipt | At the time of Purchase, we average the costs by WMAC method |
| Packaging Material costs | 3.5 | Purchase price may change for Every Goods receipt | At the time of Purchase, we average the costs by WMAC method | ||
| 2 | Operation cost | Cutting | 2.00 | Once in 6 to 12 months | Labour, Machine costs |
| Bending | 2.00 | Once in 6 to 12 months | Labour, Machine costs | ||
| Threading | 5.00 | Once in 6 to 12 months | Labour, Machine costs | ||
| Hardening | 4.00 | Once in 6 to 12 months | Labour, Machine costs | ||
| Blackening | 1.00 | Once in 6 to 12 months | Labour, Machine costs | ||
| Packaging | 1.00 | Once in 6 to 12 months | Labour, Machine costs | ||
| Total cost of Finished Good | 118.50 | ||||
| Overhead costs | 30% of total cost | 35.55 | Changes once in a year | Bill of Materials (BOM) Overhead costs | |
| Profit Margin | 30% of the total Cost including Overhead cost | 46.25 | Depending on Business Owners | Sales Decision and upload the Price Lists | |
| Total Selling price | 200.30 |
More information, click here
- Check here the ACTouch Cloud ERP Features
- How to implement an ERP Software that’s easy and quick to do?
- Problems that are faced by an ERP implementation
- Inventory cost Calculator
eMail us at sales@actouch.com for more details.
Migrate to 100% Cloud ERP Software Now and enjoy the FREEDOM | ||
 | Talk to us to know more about ACTouch Cloud ERP Software NOW  |