What is ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)?
“What is ERP?”, This is the first question many Manufacturing companies ask when they hear this word “ERP”. A definition of an ERP, Enterprise Resource Planning, is a software / tool that helps to integrate the entire business and its process on one platform. Enterprise Resource Planning can help to integrate your Production, Procurement, Supply Chain management, Sales and Finance modules. Few ERPs are extended with Human Resources and Payroll, Fixed Assets (FA) etc.
Today, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) tool is considered as accepted tool to manage the business and widely used to manage multi companies, multi branches business too.
Many consultants share “What is ERP?” like a “Magic wand” to solve all your existing Business problems, but it’s not. Also it is not a “Pain Killer” to solve all your business problems.
But Enterprise Resource Planning is like a “Vitamin”. You need to follow and be discipline to see the result. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) makes the business more of a PULL System as it makes other departments to do their work only after that remaining work happens.
There are various ways for defining Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). Enterprise Resource Planning is a software solution that helps Organisations to manage the daily business activities such as Inventory management, Sales, Procurement Management, Manufacturing, Accounting, risk management, project management, supply chain management etc.
Lets address the below questions in this article
- History of ERP
- ERP is a transaction System and not a Business intelligence one.
- ERP Benefits and why an Enterprise Resource Planning is important?
- ERP with eCommerce
- ERP Modules
- Types of Enterprise Resource Planning Systems?
- How much an Enterprise Resource Planning Costs?
- What is ERP – Conclusion – A sample ERP Application screen.
What is ERP Software? – History of ERP Evolution: How it all started?
Separate data was maintained in 1960/70’s for traditional business functions like Sales & Marketing, Finance, Human Resources, Manufacturing, and Supply Chain Management. It was difficult to manage business processes across business functions. ERP Software were developed to manage all these processes by integrating all these business functions, but it took nearly 20+ years to reach a basic version.
We as individuals cannot look forward or oversee the future without acknowledging our past. And it is no different with the history and evolution of the ERP Software. It all started back in the 1960s. With the rise in factory production demand, the need for the management of products also increased. This was also in need to keep the right balance along with maintaining the customer demands. So in order to plan and manage the complete Manufacturing process to production & delivery, Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) software was made.
By 1975 many firms were using MRP software to operate their process. The operating costs were affordable only by large businesses back then. The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software was upgraded to MRP2 software which was more sophisticated and advanced than the previous one. This upgrade took place somewhere in the 1980s which was marked again as another big milestone. MRP was focussed more on the Inventory, Sales and Purchase etc. But they didn’t address specific business cases.
The MRP2 software had more advanced production scheduling abilities which could coordinate more efficiently with various departments of the business. Then in the 1990s the more advanced version of MRP2 software came into being called the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). The idea was to have a software that takes care of every aspects of the business.
The further evolvement and advancement of the ERP software was made in the early 2000s and in today’s times the ERP system has evolved even more. The companies are utilizing the ERP system with Software as a Solution (SaaS) model as well. As the usage of the mobile applications has gone up the ERP solution are made mobile friendly as well. One can use the application from remote locations along with its web access.
Enterprise Resource Planning is a Transaction system and not a decision making system.
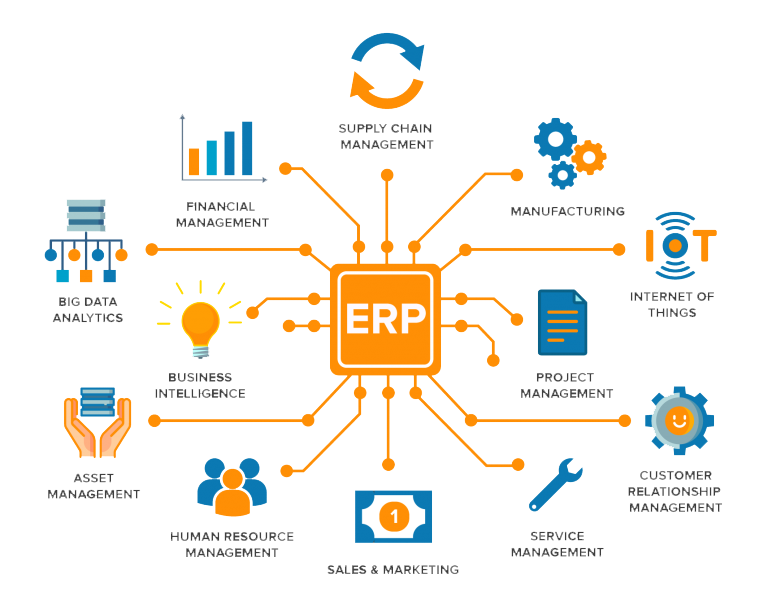
The ERP systems today have been upgraded to Extended ERP (ERP2) that was introduced by Gartner Group. The prime functionalities that the extended ERP offers are E-commerce, Supply Chain Management, Customer Relationship Management, Business Intelligence, Advance Planning and Scheduling and Internet Procurement or E-procurement.
The overall challenge of the “extended enterprise” is to ensure effectiveness of supply chains and production networks, at both national and global level. The new generation of ERP systems, the extended enterprise systems or eERP systems include the applications to support the new supply chain models. The very genesis of the eERP was to efficiently evolve from manufacturing to the entire enterprise.
It usually involves carrying out commercial transactions in a business or with an individual over the internet. This needs an infrastructure, which usually has features like catalogue, online ordering facilities and status checking facilities. The extended ERP provides this functionality seamlessly.
ERP Benefits and why an ERP is important?
Enterprise Resource Planning Software offers many business benefits, important being, it helps to streamline business communication, helps to identify the bottlenecks and bring is process standardisation. ERP helps to link many internal departments and it follows a “PULL SYSTEM” and ensure that rest of the linked departments complete their tasks before it completes its.
Enterprise Resource Planning Systems considered as the “central nervous system of Business” that controls and helps the business to operate efficiently. This means, all the business operations, data entry, report generation should happen from Enterprise Resource Planning only. If the data is kept outside the Cloud-based ERP systems, then it will not help anyone.
Example – If a “Production Department” needs RM to make a Finished Goods (FG), it has to be purchased by “Procurement department”. Once the RM comes to company, it’s received by “inventory department” and parts are “Quality checked” by QUALITY DEPARTMENT.
So each DEPARTMENT can act only after the previous department finishes it work.
Other than the major integration of business departments, it also gives many benefits.
- Improves company productivity and increase Employees moral and happiness.
- Business growth by integration and improved communication
- Improves inter department collaboration as the transparency is increased.
- Reduce inventory Wastage, helps to identify the reasons and helps to knock them off.
- Improve Customer services and happy customers.
- Better Planning and ensure that other “bottle necks” are avoided.
- MIS reports and management dashboards.
- Increases Employees happiness as their efficiency is increased now.
- Product lifecycle management with Artificial Intelligence. It increases the source of truth and data accuracy. Helps to track and convert raw materials into Finished Products.
- Real-time data processing with multiple ERP Deployment options like on-premise, Cloud or local server.
- Human capital management with managing an effective business requirements and Resources Management
- Finance module with 100% cash management with one central database for data accuracy.
- Warehouse management with material requirements with real-time visibility of order status
- Avoid manual processes and increased control on regulatory requirements to improve industry standards for manufacturing industry
- Helps to increase cost savings with real-time information.
- One common database that’s centralized database to generate all the needed reports.
Click here to read more about ERP benefits
What is ERP? – E-commerce
Supply Chain Management
Under extended Enterprise Resource Planning Software the Supply Chain Management assists in answering questions like where the good is being produced, from where the parts are to be procured and by when it has to be delivered. It assists in planning and management of production of goods.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
This usually includes customer service management and customer identification process. The ERP system provides the CRM system with the back end information. The CRM handles the lead Generation, Sales, marketing and customer service information while the ERP system takes care of the back end tasks like Order Processing, Production, Purchase shipping, tracking, billing, supply chain and accounting.
Product Life cycle Management (PLM Tools)
It enables enterprises to bring profitable products to market more effectively. It includes both the manufacturing and marketing of the good. The stage of a product life cycle determines how it has to be marketed. PLM involves all stages, including the development and manufacturing of a product, to its marketing and customer segmentation.
ERP Modules
List of Enterprise Resource Planning Software modules can be explained with a example. As we explained before, Enterprise Resource Planning helps to integrate different business departments of a company.
A Customer places an “ORDER” with a FACTORY to BUY 100 Tables.
You need a “SALES DEPT“, who interacts with this customer to make a list of items to SELL. Once the ORDER is confirmed, its handed over to “PRODUCTION DEPT” to “PLAN and MANUFACTURE“. If the STOCK is NOT in “INVENTORY DEPT“, they will raise an INDENT to “PURCHASE DEPT” to procure. When materials lands at Factory, its “QUALITY” CHECKED and “STORES Department” releases it to “PRODUCTION DEPT” to complete the manufacturing and produce the TABLES.
“FINANCE” and “DESPATCH departments” INVOICE and send the TABLES to customer. Once the MONEY RECEIVED by CUSTOMER, “FINANCE dept” takes the money into company. To manage the people at company, you need HR DEPT and they manage employees, their salary etc.
Now you know how many Departments are in a company?. In Summary, we have
- Sales and supply chain management.
- Procurement management
- Production and controls
- Planning departments
- Stores and inventory
- Finance department
- Quality
- HR Department
- Despatch and logistics department.
In summary, an ERP can have ALL the above or FEW modules.
Types of ERP Systems
ERP systems are many and each ERP has different business verticals to focus and help. Many customers, who are afraid of loosing the data or afraid of data theft, prefer to go for “ON-PREMISE ERP”, while the rest can try for “CLOUD ERP”. Cloud ERP helps to save money, save on resources and ensure that best of the support staffs available to help.
Cloud ERP mainly helps to reduce the CAPEX investment to OPEX investment as you pay less money for a good ERP Software.
Below are based on Manufacturing Types and how the functionality can be suited for each of the below types.
- Discrete Manufacturing ERP
- Process manufacturing ERP
- Project Based ERP
- Textiles ERP
- Real Estate ERPs
Depending on the SIZE of company and complexity of Business, we can decide to select different types of ERPs.
A sample manufacturing process with multi level BOMs, Work centre with a clearly defined Process.
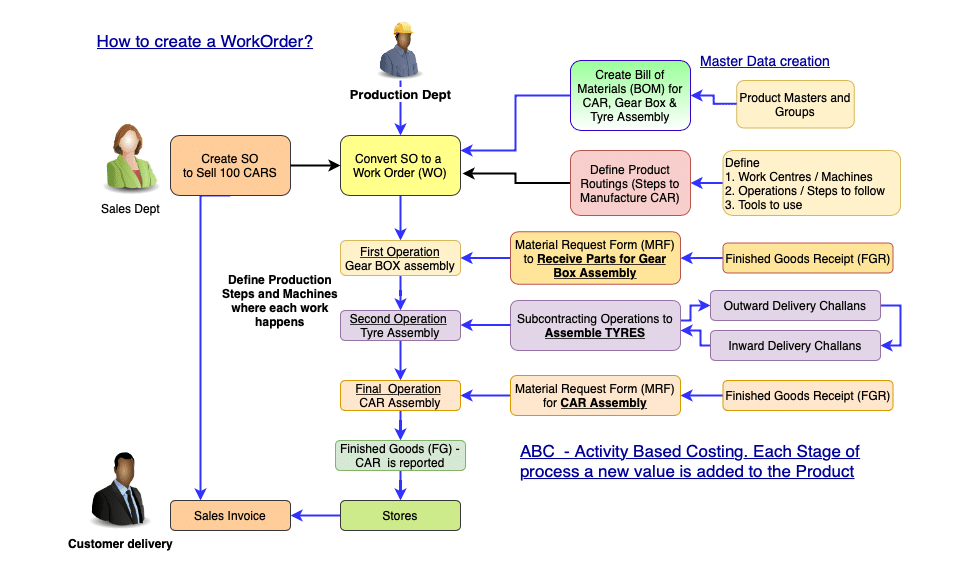
Based on your Budget, Features and Functionalities
Even though ERPs are designed to handle SIMPLE to COMPLEX process, each Manufacturing Companies have their standard process to follow and many of them are SAME. Starting from “Procurement”, “Sales”, “Production”, “HR”, “Finance”, “Inventory Management” etc.
Whether a company has LESS BUDGET or LARGE BUDGET, they need an ERP with the above features.
Type of enterprises – Small, Medium and Large Enterprises
Large Enterprises can go for SAP Hana or Oracle or NetSUITE etc. But as we explained earlier, SMBs can decide to go for lesser known ERPs that provides a quality features at an affordable prices. Few factors that affects a selection of an ERP are
- Cost of ERP – Whats my total cost in 10 years?
- Complexity of product and features- Do I need this complex?
- Maintenance of the ERP on regular basis
- Availability of resources
- Migration process.
- ERP Integration with other Tools.
How much is an ERP System Costs?
ERP Software Costs is depending on many factors. It depends on each software vendor and its reputation and other users of same software.
Major cost is depending on the below parameters.
- The Deployment of ERP – Is it “On-premise” or “Cloud Based” deployment – Traditionally, Cloud Deployment is cheaper than “On-premise” model. Also the cost of Cloud deployment is ANNUAL and not paid in LUMP SUM
- User license costs – Depending on how many Users and each users license costs.
- Implementation fees – Helps to Configure and implement ERP as per customer needs. It involves end user training, Testing support and go live support.
- Customisation charges – few cases, standard ERP has to be customised to meet Customers specific needs.
- Any other incidental costs for the implementation.
If you prefer to go for “On-Premise” ERP deployment, then you need to plan for the below
- On-premise Server Costs – The ERP server, its configuration etc to be maintained by customer. You need to take regular Database and Application backups.
- Local Network and access to Server
- IT Person salary as someone to maintain the sever and ensure it works properly.
- Regular Software and Hardware maintenance costs.
Considering the above, its wise to come with a total costing details for 10 yeas span and decide which one suits your need.
What is ERP System? – A Conclusion
The ERP system basically allows companies to decrease the time it takes companies to get paid for its goods or services after sale. The ERP systems increases productivity by integrating the data and processes across multiple locations and departments which allows companies to move products faster, process orders quicker and invoice customers more aptly and dispatch the shipments sooner.
The organisations should take the necessary precautions while choosing the correct ERP systems. Choosing the right ERP system allows for an increased cash flow and enhanced productivity. The resulting time taken to implement the ERP system depends on the size of the business, different departments involved, customization involved and the timely cooperation of the customers to the project.
Adopting ERP eradicates the problem of coordination between many systems and also ensures communication, productivity and efficiency. The ERP system enables the company to stay ahead of its competitors and organises customer experience through quick problem resolution.
Realising all these factors the SMEs have started implementing the ERP systems to compete successfully in the changing business environment. There are many cloud ERP Software like SAP B1, TCS iON, ACTouch etc thats focussed on Manufacturing segments.
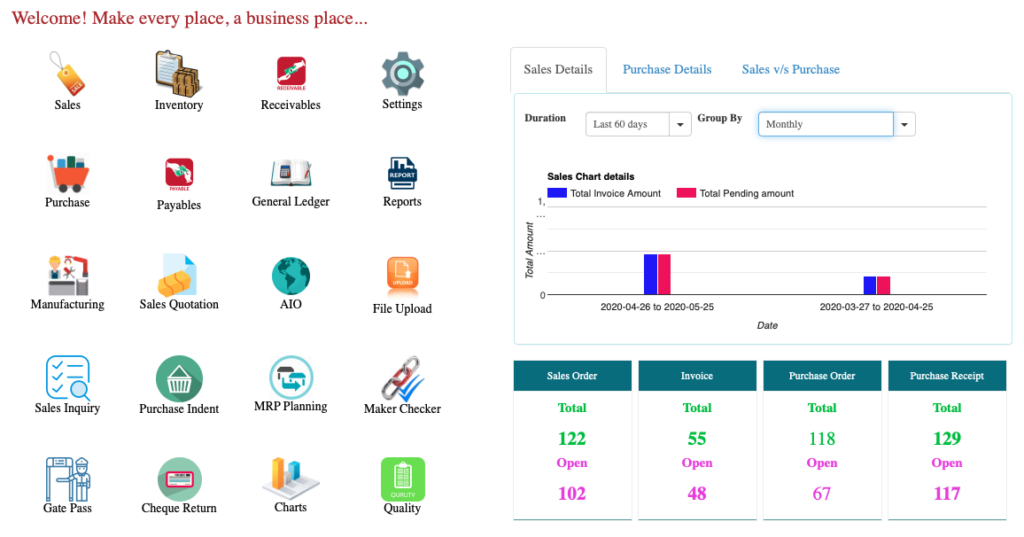
A ERP Dashboard with all the Features and Functionalities.