Finished Goods Receipt (FGR)
When we do a Finished Goods Receipt (FGR) / Semi Finished Goods Receipt (Semi FG), we consume the Raw Materials (RM) or Semi Finished Goods that are related to the same FG. This menu helps us to report the FG and also check the RM consumed as part of this process. Bill of Materials helps us to pre-define the RMs that are essential for the processing.
In this process, we do the following work.
- FG Report – When we report a FG, we follow ABC (Activity based costing) model to arrive at the product costing. So FGR process helps to book the product cost including other incidental costs.
- Consume RM that are part of this FG
- Report By-products that has some values and this could be reused.
The FG cost is the combination of the following components.
- RM costs – The materials that are consumed to arrive at the Finished Goods.
- Labour, Machine, Overhead and other costs that are added to FG costs.
- By-products cost – This costs is reduced from the RM costs to give an actual materials consumption for the FG.
Stock management happens as below during FGR process.
- FG stock is added to inventory
- RM are reduced
- By-products are added to the Inventory.
Note: Many customers doesn’t want to REPORT Production work, but want to bring the FG into ERP for Sales. But the challenge here is, the RM consumption has to be done manually. So defining the BOM and reporting the FG will help to manage the inventory more easily and efficiently.
Field Details of FGR process.
Before you report the FGR of the FG, we need the following details made available.
- Product Masters
- BOM – Bill of Materials
- Locations where the stock is kept.
- Operator Details, if required at (Employee Master)
- Scrap and Reject Reasons.
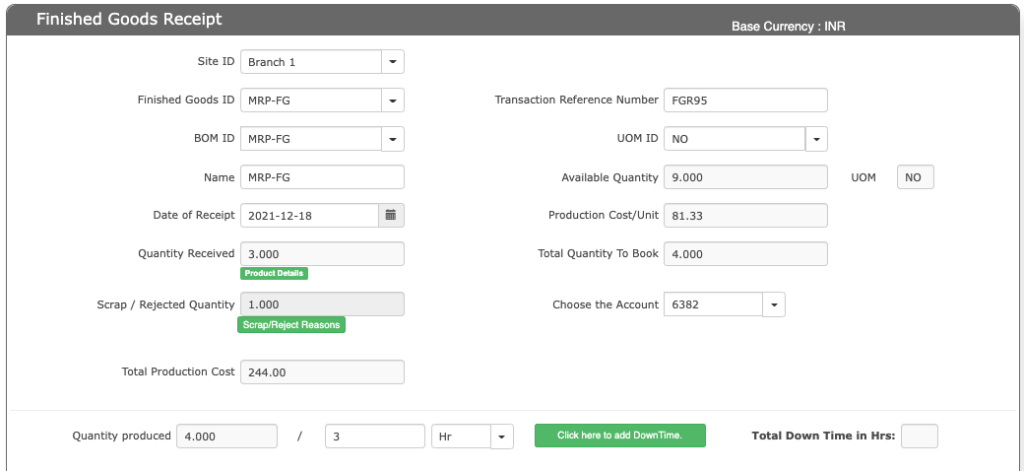
| No | Field ID | Field name | Mandatory | Field description and how it helps? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Finished goods ID | FG ID | Yes | It is the unique identification number given to each Finished goods. |
| 2. | BOM ID | BOM ID | Yes | It is the unique identification number given to each Bill of Material. Here based on the FG ID, the BOM ids are shown. |
| 3. | Name | Name of the Finished Goods | Yes | Name of the finished goods. |
| 4. | Date of Receipt | Date of receipt | Yes | Date on which the Finished goods prouction is reported. |
| 5. | Quantity Received | Total quantity received | Yes | Total quantity of the Finished goods received. |
| 6. | Scrap/Rejected Quantity | Scrap quantity | Yes | Total number of SCRAPS / REJECTION of FG that’s happened. Here the total RMs are combination of “GOOD QTY” and “REJECTED QTY”. Note – The “REJECTED QUANTITY” cost is distributed to FG. |
| 7. | Total Production Cost | Production cost | Yes | Total cost incurred for converting the Raw material to the finished goods. |
| 8. | Transaction Reference Number | FGR ID | Yes | It is the Document Number given to the FG for internal reference. |
| 9. | UOM ID | Unit Of Measure ID | Yes | FG’s Units Of Measurement in which the production is reported. |
| 10. | Available Quantity | Total quantity of finished goods available | Yes | It gives the total quantity of the finished goods available. |
| 11. | UOM | Unit of measure | Yes | It is the magnitude of the quantity.It can be kg, litre, etc. |
| 12. | Production Cost/Unit | Total Production Cost/Unit | Yes | It gives the total cost incurred for producing one unit of the finished goods. |
| 13. | Total Quantity To Book | Total Quantity To Book | Yes | It gives us the total quantity of the finished goods that is booked. |
| 14. | Choose Account | Account code | No | It gives the particular account code for the production cost. |
| 15. | Enable Multiple Operators | Multiple operators enabling option | No | It gives an option for enabling multiple operators who work in different shifts basis. The Costs of these operators are added as “LABOR COST” to FG. You can set up these employees at “Employee Master” |
| 16. | Operator ID | Unique identification number for Operators | No | In case, you have a single Operator who works on this process, then mention that Operator ID. This is used to know the Operator production details later. |
In this section, we capture below details that are essential for the business.
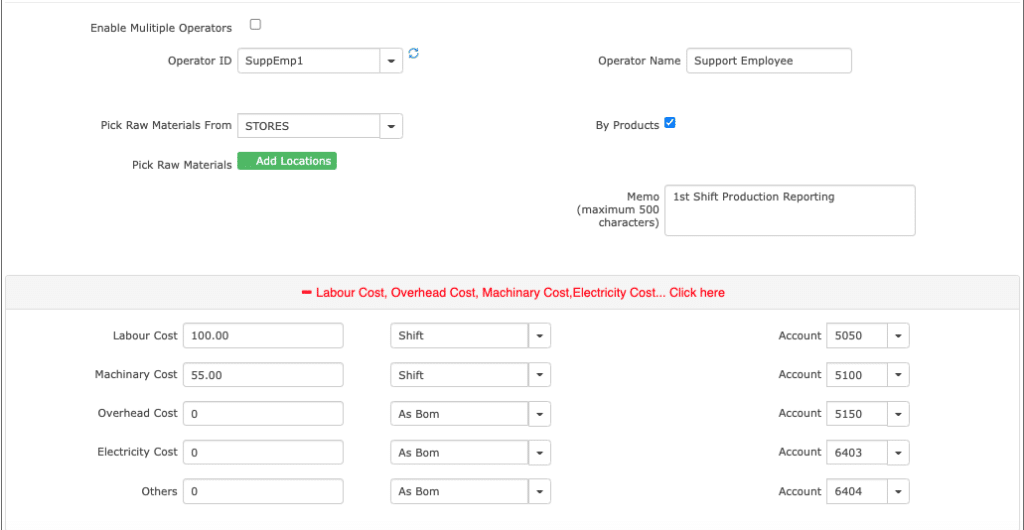
Based on the Operator and other details can be added based on the need like Scrap and Reject items, Labor Costs, Machinery costs, Overhead costs etc.
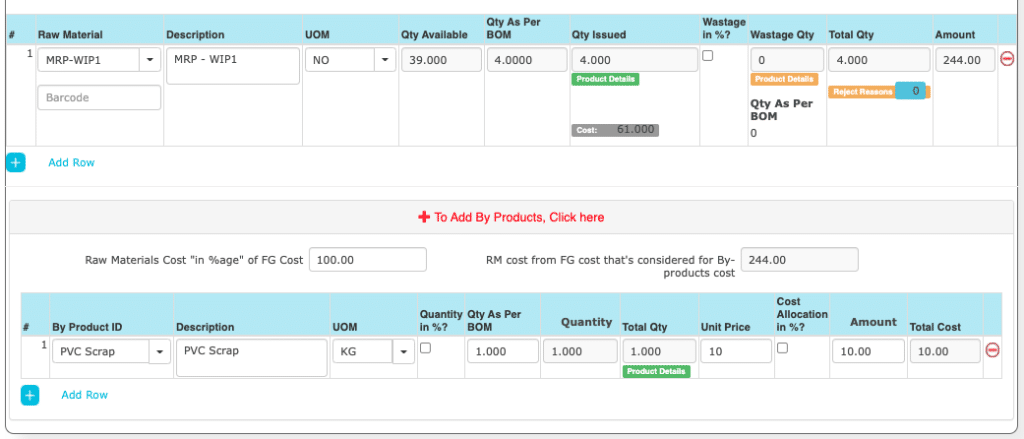
Enter the RM that’s consumed, additional materials consumed are entered. You can enter the by-product and its costing can be captured.
As part of this.
- You report the consumption of Raw Materials, its UOM and Quantity
- Report wastage quantity, if needed.
- Enter the By-Products, its Quantity, Unit cost etc. This will be added to Inventory.
| 17. | Operator Name | Name of the Operator | No | Name of the Operator who is working on the machine. |
| 18. | By-Products | By-products option | No | Its gives an option to select if any By-Product is produced while working on the raw material. |
| 19. | Memo | Memo. | No | It briefly describes the work done by the particular operator on the given raw material on that particular day. |
| 20. | Labour Cost | Cost of labour | No | It gives us the total cost of labour to work on the raw material given. |
| 21. | Machinery Cost | Cost of machinery | No | It gives the cost of using the machinery to convert the raw material into a finished goods. |
| 22. | Overhead Cost | Operating expenses | No | It gives those cost expenditures not directly related to the product but are incurred such as rent etc. |
| 23. | Electricity Cost | Cost of electricity usage | No | It gives the cost of the electricity used to produce the finished goods. |
| 24. | Others | Miscellaneous cost | No | It gives miscellaneous cost incurred while making the finished goods. |
| 25. | Accounts for each of the above types | Account code | No | It gives the account code for a particular account name.Example: 5050 for labour costs (COGS). |
| 26. | Raw material ID | Raw material identification number | Yes | It is the unique identification number given to each raw material. |
| 27. | Description | Raw material description | Yes | RM Names |
| 28. | UOM | Unit of measure | Yes | Units of measurement. |
| 29. | Quantity | Quantity | Yes | Enter the RM consumed. |
| 30. | Wastage in % | Percentage Wastage of the raw material | Yes | It gives an option to define whether the WASTAGE is in percentage of raw material while producing the finished goods or in absolute Numbers. |
| 31. | Wastage Qty | Quantity of wastage | Yes | Total Quantity of Wastage accrued while producing the finished goods. |
| 32. | Total Qty | Total quantity of the raw material used. | Yes | It gives the total quantity of the raw material used to develop a finished goods. |
| 33. | Reject Reasons | Reason for rejection | No | It describes the reason for rejection of the particular raw material. It contains fields such as type, reason, description and quantity. |
| 34. | Type | Type of reason for rejection | No | It gives two options to choose between i.e., Scrap or Reject.Raw material to be treated as Scrap or to Reject the raw material altogether. |
| 35. | Reason | Specific Reason | No | We need to provide the specific reason for Rejection or for treating a particular raw material as Scrap. |
| 36. | Description | Brief Description | No | It gives the brief description for the particular reason that has been provided for Rejection or treating the raw material as Scrap. |
| 37. | Qty | Quantity of raw material | Yes | It gives the total quantity of the raw material treated as Rejected or as Scrap. |
| 34. | Unit Price | Price of a single unit of raw material | Yes | It gives the price of one single unit of the raw material used for making a finished goods. |
| 35. | Line Total | Total price of the raw material used | Yes | It gives the total amount of the particular raw material used.Total Qty*Unit Price = Line Total |
| 36. | RM Cost Percentage | Raw material cost in percentage | Yes | It gives the total amount of the raw material used in percentage. |
| 37. | By Product ID | By Product identification number | Yes | It is the unique identification number given to the By-products obtained while making a finished goods. |
| 38. | Description | By-product description | Yes | By-products description. |
| 39. | Quantity in % | By-product quantity in percentage | Yes | It gives us the percentage of By-product produced while producing the finished goods. If this is field is not selected then we will be directly taking the magnitude of quantity of the by-product into consideration ignoring the percentage quantity of the by-product. |
| 40. | Percentage | Percentage of the quantity | Yes | It gives what percentage of the quantity is assigned to the by-product. |
| 41. | Quantity | Quantity of the by-product | Yes | It gives the total magnitude of quantity of the by-product we get after calculation of percentage of the quantity. |
| 42. | Cost Allocation in % | Allocation of cost in percentage | Yes | The total amount allocated for the by-product in percentage value. If this field is not selected then we directly take the magnitude of the cost allocated for the by-product. |
| 43. | Cost in Amount/Percentage | Total cost in amount or percentage | Yes | It gives the total cost of the by-product in amount / percentage. If the cost allocation in % field is selected then we will get the cost in percentage otherwise we get the cost in amount. |
| 44. | Raw Materials Cost “in %age” of FG Cost | Total cost of Raw Materials “in %age” of FG Cost | Yes | It provides the total cost of the Raw Materials (RM) in percentage of the Finished Goods (FG) Cost. |
| 45. | RM cost from FG cost that’s considered for By-products cost | RM cost from FG cost that’s considered for By-Products cost | Yes | It gives the cost of Raw Material (RM) used for By Products from the Finished Goods (FG) Cost. |
You have an option to UPDATE the FGR Document to change the quantity or any parameters, if any.