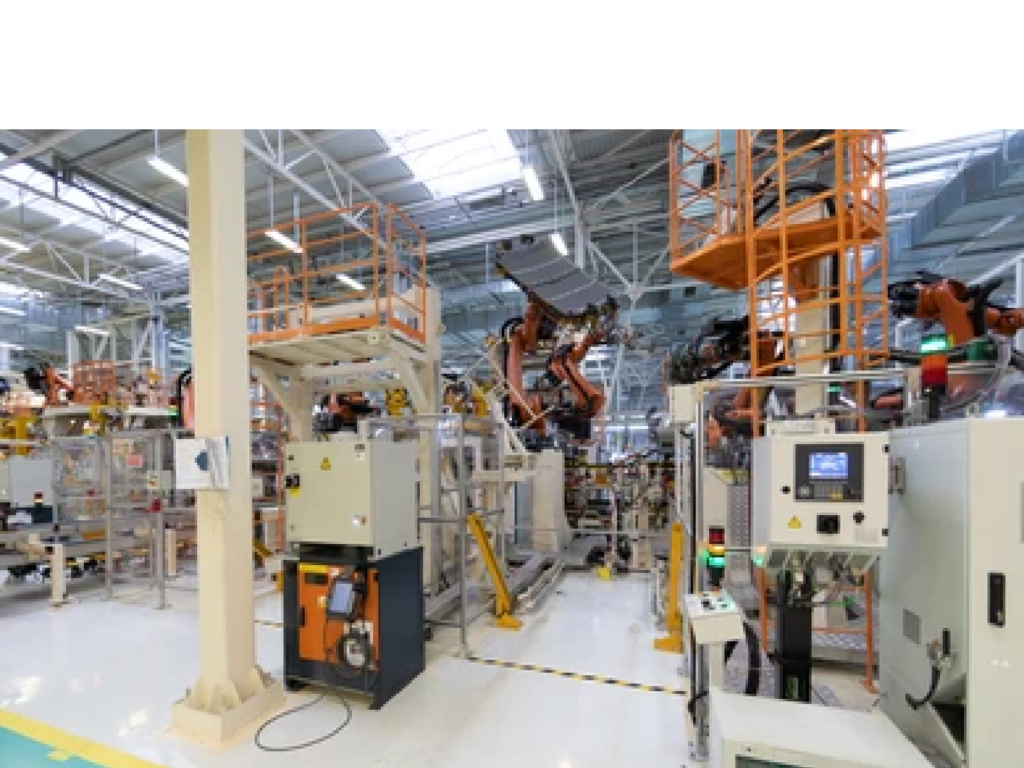
The Power of Manufacturing Automation
What is Automation?
Automation refers to the use of technology and advanced systems to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. It involves the creation of processes that are self-executing, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing overall efficiency. In the context of manufacturing, automation plays a pivotal role in transforming traditional production methods into highly optimized and streamlined operations.
Most of CNC or VMC Machines have a Programmable automation ability and also gives a Flexible automation model to do multi tasks and machining work. Based on machine programming you can use the it for production.
Manufacturing industry like automotive industry have built a complex form of automation with automatic controls to manage forging production, special assembly process which are controlled by special computers to achieve targets etc. Few machines are still controlled by analog control systems as they could not be moved to CNC programming.
What is Automation in manufacturing Process?
Automation in the Manufacturing process refers to the integration of various technologies and tools to automate production tasks, reducing the dependency on manual labor and enhancing overall productivity. This automation covers a wide range of activities, such as assembly line operations, material handling, quality control, and even administrative tasks.
What are the different types of Manufacturing Automation, we see today?
Robotics and Robotic Automation
Robots are extensively used in modern manufacturing facilities to perform repetitive and labor-intensive tasks with precision and speed. They can handle tasks ranging from welding and painting to material handling and packaging.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machines
CNC machines are automated tools that can be programmed to perform precise tasks like cutting, drilling, and shaping various materials. They offer increased accuracy and consistency in manufacturing processes.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs are autonomous vehicles used for material transportation within the factory premises. They can navigate through designated paths and avoid obstacles, ensuring a smooth and efficient material flow.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
IoT and IIoT technologies enable the integration and communication of various devices and systems, allowing real-time monitoring, data analysis, and predictive maintenance, leading to optimized operations.
Automated Assembly Systems
These systems automate the assembly of products, reducing manual labor and minimizing errors, thereby enhancing the overall quality and productivity.
Benefits of Manufacturing Automation
Production Automation or Automation in Manufacturing helps to increase productivity and reduces human errors. It reduces dependency in humans, while it improves quality output and its speed of delivery.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Manufacturing automation reduces cycle times, minimizes downtime, and optimizes resource utilization, resulting in increased production output and overall efficiency.
Enhanced Quality and Consistency
Automation ensures precise execution of tasks, leading to higher product quality and consistency. It significantly reduces defects and variations, which can positively impact a company’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
Cost Reduction
While initial investments in automation might be significant, the long-term benefits include reduced labor costs, minimized wastage, and lower maintenance expenses. Over time, the return on investment can be substantial.
Improved Workplace Safety
Automation eliminates the need for humans to perform hazardous tasks, thereby reducing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries. Employees can be assigned to more value-added roles that require creativity and critical thinking.
Faster Time-to-Market
Automation streamlines the manufacturing process, reducing lead times and enabling companies to bring their products to the market faster, gaining a competitive edge.
Flexibility and Scalability
Modern manufacturing automation systems are designed to be flexible and easily adaptable to changes in production requirements. This scalability allows businesses to ramp up or down production as needed, responding quickly to market demands.
|
How Manufacturing Automation Process works with Cloud ERP Software?
The integration of Manufacturing Automation with Cloud Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software brings unparalleled advantages to businesses. Cloud ERP systems provide a centralized platform that facilitates seamless data sharing, analysis, and decision-making across the organization. When combined with Manufacturing Automation, the benefits are further enhanced:
Real-time Data Insights
Cloud ERP systems enable real-time data collection and analysis from automated manufacturing processes. This data helps managers make informed decisions, identify bottlenecks, and optimize production flows.
Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud-based ERP solutions allow employees from different departments and even remote locations to access and share information, fostering better collaboration and communication.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Cloud ERP, when integrated with IIoT devices, enables remote monitoring and control of manufacturing processes. Managers can monitor production activities and intervene if necessary, even when off-site.
Predictive Maintenance
By leveraging data from automated machines and IoT sensors, Cloud ERP systems can facilitate predictive maintenance. This helps identify potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Inventory Optimisation
With automation and Cloud ERP integration, businesses can maintain real-time inventory tracking, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.
What is Industrial automation process?
Industrial automation process refers to the implementation of automation technology in industrial settings to streamline and optimize manufacturing and production processes. It involves the integration of various technologies to control and monitor machinery, equipment, and processes, reducing human involvement while improving operational efficiency and product quality.
The industrial automation process typically involves the following steps:
- Analysis: Assessing the existing processes and identifying tasks suitable for automation.
- Design: Creating a plan for implementing automation solutions, including hardware and software components.
- Integration: Installing and configuring automation equipment and systems, including sensors, controllers, and communication networks.
- Programming: Developing the necessary software logic and algorithms to control and coordinate automated processes.
- Testing: Verifying the functionality and performance of the automation system through simulations and real-world testing.
- Implementation: Deploying the automation solution in the production environment and fine-tuning as needed.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitoring the system’s performance, making adjustments, and performing maintenance to ensure smooth operation.
Industrial automation process benefits industries by increasing production rates, improving product quality consistency, reducing waste and errors, enhancing safety for workers, and enabling rapid adaptation to changing market demands.
More on Automated Manufacturing system.
An automated manufacturing system is a complex arrangement of machinery, equipment, software, and processes designed to perform manufacturing tasks with minimal human intervention. Its purpose is to create a highly efficient and flexible production environment that can produce goods at a faster rate, with greater accuracy, and with the ability to adapt to changes in product specifications or demand.
Key components of an automated manufacturing system include:
- Robotic Systems: Robotic arms and devices capable of performing various tasks, such as assembly, welding, painting, and material handling.
- Sensors and Vision Systems: Sensors for detecting physical variables like temperature, pressure, and position, as well as vision systems for quality control and inspection.
- Controllers and PLCs: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and other control systems that manage and coordinate the actions of different components within the system.
- Conveyor Systems: Automated conveyor belts or other transport systems that move materials and products between different stages of the production process.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): Interfaces that allow operators to monitor and interact with the automated system, providing input and receiving feedback.
- Data Analytics and Connectivity: Technologies that gather and analyze data from various sensors and devices to optimize production processes and facilitate decision-making.
Automated manufacturing systems are designed to handle repetitive tasks, reduce errors, increase production capacity, and improve overall product quality. They are essential in industries where efficiency, precision, and flexibility are paramount, such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods.
What is the Future Automated Factory design, it’s workings?
The future automated factory refers to the vision of advanced manufacturing facilities where automation technologies, artificial intelligence, robotics, data analytics, and connectivity converge to create highly efficient, flexible, and adaptable production environments. In such factories, processes are streamlined, and various tasks are executed by machines and systems with minimal human intervention.
Key features of the future automated factory might include:
- Smart Manufacturing: Integration of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to enable machines, sensors, and devices to communicate and share data in real time for improved decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Implementation of AI algorithms that allow machines to learn and optimize processes, as well as make intelligent decisions based on data analysis.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Robots designed to work alongside humans, facilitating a safer and more collaborative working environment.
- Flexible Production Lines: Setups that can quickly adapt to changing product specifications and demand, allowing for efficient production of diverse products.
- Autonomous Systems: Machinery and vehicles capable of autonomous navigation and operation, reducing the need for constant human supervision.
- Customization and Personalization: Advanced automation systems that can produce customized products on-demand without significantly disrupting the production process.
- Sustainability: Integration of energy-efficient technologies and sustainable practices to reduce waste, energy consumption, and environmental impact.
The future automated factory is driven by ongoing advancements in automation technology, AI, robotics, and connectivity. It aims to revolutionize manufacturing by improving efficiency, quality, and sustainability, ultimately reshaping industries and the global economy.
FAQ on Manufacturing Automation
1. What is automation in manufacturing?
Automation in manufacturing refers to the use of computer-controlled machines, robots, and other advanced technologies to perform tasks that were previously done by human operators. It involves the integration of smart systems and machines to streamline production processes, increase efficiency, and reduce human intervention.
2. What are the benefits of automation in manufacturing?
Automation offers several benefits, including:
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Improved product quality and consistency
- Reduced production costs
- Enhanced workplace safety by replacing humans in hazardous tasks
- Greater flexibility in production schedules
- Faster production turnaround times
- Ability to handle complex and repetitive tasks with precision
3. What types of tasks can be automated in manufacturing?
Various tasks in manufacturing can be automated, including:
- Assembly of products
- Material handling and transfer
- Quality control and inspection
- Welding and cutting operations
- Packaging and labeling
- Inventory management and tracking
- Machine loading and unloading
- Data collection and analysis for process optimisation
4. How does automation impact the workforce in manufacturing?
Automation can lead to workforce transformation. While it may reduce the need for some manual labor, it also creates new job opportunities in areas like maintenance, programming, and system supervision. Workers may need to upskill or transition to roles that require more advanced technical knowledge.
5. What are the challenges of implementing automation in manufacturing?
Challenges of implementing automation include:
- High initial investment in technology and training
- Integration with existing systems and equipment
- Reskilling the workforce to adapt to automation
- Potential job displacement and worker resistance
- Cybersecurity concerns for connected systems
- Balancing human-machine collaboration for optimal results
- Regular maintenance and upgrades to keep automation systems efficient and functional
6. How does automation improve quality control in manufacturing?
Automation enhances quality control by performing consistent and accurate inspections at high speeds. Automated systems use sensors and cameras to detect defects, deviations, or variations in products, ensuring that faulty items are identified and rejected early in the production process.
7. Can small and medium-sized manufacturers benefit from automation?
Yes, automation is not limited to large corporations. Small and medium-sized manufacturers can benefit from automation by focusing on specific processes or tasks that can be effectively automated. There are various cost-effective automation solutions tailored to the needs of smaller businesses.
8. How can automation contribute to sustainability in manufacturing?
Automation can help improve sustainability in manufacturing by optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and lowering energy consumption. Smart manufacturing processes can minimize environmental impacts and enhance overall eco-efficiency.
9. Are there risks associated with automation in manufacturing?
While automation offers significant advantages, there are potential risks, including:
- Cybersecurity threats to connected systems
- Over-reliance on automation, leading to a lack of human oversight
- Potential job displacement and worker dissatisfaction
- Technical failures and downtime affecting production
10. What is the future of automation in manufacturing?
The future of automation in manufacturing is likely to involve more advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and collaborative robotics. Automation will continue to play a crucial role in increasing efficiency, agility, and sustainability in the manufacturing industry.
11. What are the best practices for implementing Manufacturing Automation?
The best practices for implementing Manufacturing Automation include conducting a thorough process analysis, identifying suitable technologies, ensuring proper training for employees, and starting with small-scale pilot projects before full-scale implementation.
12. How can Manufacturing Automation improve product quality?
Automation ensures consistent and precise execution of tasks, reducing the risk of human errors and defects. This, in turn, leads to improved product quality and customer satisfaction.
13. Will implementing Automation lead to job losses in the manufacturing sector?
While automation may replace some manual tasks, it also creates new job opportunities in roles like system maintenance, programming, and data analysis. Additionally, it allows employees to focus on more complex and creative tasks.
14. How secure is cloud-based ERP when it comes to sensitive manufacturing data?
Cloud ERP providers invest heavily in security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular backups. They adhere to industry standards to ensure the protection of sensitive manufacturing data.
15. Can smaller manufacturing businesses afford to invest in Automation?
Yes, with advancements in technology, automation solutions have become more affordable and scalable. Smaller businesses can start with specific automated processes and gradually expand as they experience the benefits and grow their operations.
16. What is factory automation?
Factory automation refers to the use of various technologies, control systems, and equipment to perform tasks in a manufacturing or production environment with minimal human intervention. The primary goal of factory automation is to improve efficiency, productivity, quality, and safety while reducing costs and human error. It involves the integration of machinery, software, sensors, and communication networks to streamline manufacturing processes. This can range from simple automated tasks, such as robotic arms assembling products, to complex interconnected systems managing the entire production line.
In a factory automation setup, various components work together seamlessly to execute tasks that were previously done manually. These components may include robotic arms, conveyor systems, sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and data analytics software. By automating repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, factories can achieve higher output rates, tighter quality control, and the ability to adapt to changes in demand or product specifications more efficiently.
17. What is the meaning of automation?
Automation refers to the process of using technology and control systems to perform tasks without direct human intervention. It involves the design, development, and implementation of systems that can execute predefined actions or processes with minimal human oversight. The primary objective of automation is to enhance efficiency, accuracy, consistency, and speed in various operations while reducing the reliance on manual labor.
Automation can be applied in various domains, including manufacturing, logistics, information technology, agriculture, healthcare, and more. It involves integrating hardware, software, sensors, and communication technologies to create systems that can respond to specific conditions, follow programmed instructions, and make decisions based on predefined criteria. Automation can range from simple tasks, such as automatic email replies, to complex processes like self-driving cars navigating through traffic.
18. Explain about automation equipment manufacturers
Automation equipment manufacturers are companies that specialize in designing, producing, and supplying machinery, devices, and systems used in automation processes across various industries. These manufacturers play a crucial role in advancing industrial automation by developing cutting-edge technologies and solutions that improve productivity and operational efficiency. Their products are used to automate tasks that were traditionally performed manually or semi-manually.
These manufacturers produce a wide range of automation equipment, including robotic systems, conveyors, sensors, actuators, vision systems, controllers, and other specialized hardware and software components. They often collaborate with industries such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and more, tailoring their products to specific application requirements. Automation equipment manufacturers are essential in shaping the landscape of modern manufacturing and driving innovation in areas like robotics, artificial intelligence, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
19. What is automation technology?
Automation technology encompasses the tools, techniques, and systems used to implement automation in various processes and industries. It encompasses a wide range of technologies, including robotics, control systems, sensors, actuators, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics. Automation technology aims to create systems that can operate autonomously, following predefined instructions and adapting to changing conditions as needed.
Automation technology involves integrating hardware and software components to enable communication, decision-making, and execution of tasks without human intervention. For example, in industrial settings, automation technology can involve the use of PLCs to control machinery, robotic arms for assembling products, and sensors to monitor production variables. Advanced automation technologies, such as machine learning algorithms and AI-driven systems, enable automation to become more adaptive and capable of learning from data.
Manufacturing Automation is a powerful force that drives efficiency, productivity, and innovation in the manufacturing industry. By leveraging advanced technologies such as robotics, IoT, and cloud-based ERP systems, businesses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition. Embracing automation not only improves the bottom line but also creates safer and more rewarding work environments for employees. To unlock the full potential of Manufacturing Automation, businesses must carefully analyze their processes, identify suitable technologies, and invest in the necessary training and infrastructure.